Magnetism
Magnetic Field
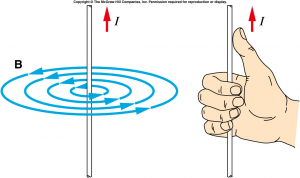
A moving charge causes a magnetic field, following the right hand rule: Your thumb pointing towards the direction of movement of the positive charge, and your other fingers wrap around to indicate the direction of the magnetic field.
A circulating current forms a magnetic dipole.
Calculate Field
Where is magnetic permeability, and is distance from the wire.
Any component going along the direction of current is cancelled by cross product. Something else. Therefore, it is unsurprising that magnetic field is circulating.
Special Field: Wire
- TODO: Later fill out <01-03-24, xydxydxyd1> -
Loops
Let there be a loop of current flowing clockwise. The magnetic field inside the loop is always going out of the page, whereas the field outside always go into the page.
This can be proven by considering each single length of wire. The shape of the loop does not matter.
Ampere's Law of Magnetic field
The general proof of Ampere's Law involves starting from Biot-Savart Law, integrating to a term and a Maxwell's term. I will do the proof later.
Uniform Magnetic Field
A pair of current loops can create a very uniform magnetic field in the middle.
Solenoid
Solenoid is a very useful way to create magnetic fields. They are essentially a long coil of current. Inside the solenoid there is a strong, uniform magnetic field. At the ends, the strength drop drastically.
The field created can be derived from adding together circular loops.





