Neural network
A neural network is a type of machine learning model that utilizes layers of connected neurons to perform classification and regression.
Structure
Neuron
The neuron is the data-processing unit that composes a neural network. It combines information from multiple neurons (or input) and become activated or deactivated. The output is determined by the following steps:
- A neuron generates a linear combination of input data, z. This is done with a set of weights.
- z is fed into an activation function
- The activation function determines whether the neuron is activated (1) or not (0)
Layers
Many neurons form a layer, and many layers form a neural network. Each neuron takes input from neurons of the previous layer, and send outputs to the next layer.
The first layer of an NN is the input layer. In contrast to other layers, each neuron in the input layer takes one attribute as their input. As such, the size of the input layer is the same as the number of attributes used to train the model.
The last layer of an NN is the output layer. Pretty self explanatory.
Any layer in between are called hidden layers.
Training
Training of a neural network consists of feed-forward passes to compute the network output and back propagation to calculate the error.
Loss function
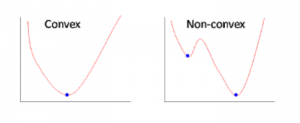
The loss function in ANN is usually non-convex, making minimization more difficult than setting the gradient to 0.
Constraints
Neural network relies on the input being standardized and numerical. One-hot encoding and label encoding can help encode categorical data into numerical ones.
Neural networks are robust and resilient to noise. They are also good at handling non-linear stuff.
On the other hand, they are somewhat a black box, computationally expensive, and prone to overfitting.
Classification
The number of layers and the size of each layer determines the complexity of the model.
- Artificial neural network has 3 layers
- Deep neural network has a lot of layers.
Output Encoding
The output layer of the network is encoded into the output.
1-of-n output encoding selects one neuron as the output from a set of probability-quantified neurons in the output layer.
One-output node has a single neuron at the output layer. It is useful for binary classification or when outputs are ordered.
