Second Order Circuits: Difference between revisions
From Rice Wiki
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Second order circuits''' are circuits that have two energy storage | '''Second order circuits''' are circuits that have two energy storage | ||
elements, resultingin second-order differential equations. | elements, resultingin second-order differential equations. There are | ||
primarily two types: | |||
* Parallel RLC circuits | |||
* Series RLC circuits | |||
= Series RLC Circuits = | |||
== Unforced == | |||
[[File:Unforced RLC Circuit.png|thumb|An unforced RLC circuit]] | |||
Consider an un-forced RLC circuit. We want to find <math>V_C</math>. | Consider an un-forced RLC circuit. We want to find <math>V_C</math>. | ||
Revision as of 06:50, 8 March 2024
Second order circuits are circuits that have two energy storage elements, resultingin second-order differential equations. There are primarily two types:
- Parallel RLC circuits
- Series RLC circuits
Series RLC Circuits
Unforced
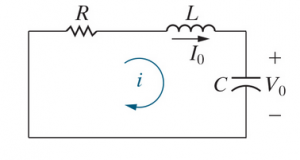
Consider an un-forced RLC circuit. We want to find .
First, we can use KVL and KCL
Next, we can use and substitution to get
Changing the order and moving the constants,
Moving constants away from the first term to get a second-order differential equation,







