Skewness: Difference between revisions
From Rice Wiki
(Created page with "The '''skewness''' of a dataset determines the direction of the outliers. = Impact = Many models assume the data to be normally distributed. Skewed data in those models will result in inaccurate predictions. = Detection = Data skewness is detected during Exploratory data analysis. The first method is visualization. Just look at a graph lol. Numerically, in a dataset, if the median < the mean, then it is skewed to the right. Vice versa. = Mitigate pr...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
= Mitigate problems = | = Mitigate problems = | ||
[[File:Skewness mitigation.png|thumb|Figure 1. Effects of log, square root, and inverse transformations on skewed data]] | |||
Skewed data can be transformed to approximate a more symmetric distribution. Examples include logarithmic, square root, and inverse transformations. | Skewed data can be transformed to approximate a more symmetric distribution. Examples include logarithmic, square root, and inverse transformations. | ||
[[Category:Machine Learning]] | [[Category:Machine Learning]] | ||
Revision as of 06:46, 26 April 2024
The skewness of a dataset determines the direction of the outliers.
Impact
Many models assume the data to be normally distributed. Skewed data in those models will result in inaccurate predictions.
Detection
Data skewness is detected during Exploratory data analysis.
The first method is visualization. Just look at a graph lol.
Numerically, in a dataset, if the median < the mean, then it is skewed to the right. Vice versa.
Mitigate problems
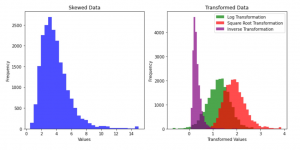
Skewed data can be transformed to approximate a more symmetric distribution. Examples include logarithmic, square root, and inverse transformations.
