Thread: Difference between revisions
From Rice Wiki
(Created page with "A '''thread''' in Computer Science is defined as a sequence of executing instructions from a program. Notably, it is active/running. Category:Operating System") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A '''thread''' in Computer Science is defined as a sequence of executing instructions from a program. Notably, it is active/running. | [[File:OSTEP 26.1.png|thumb|Credits to OSTEP textbook]] | ||
A '''thread''' in Computer Science is defined as a sequence of executing instructions from a program. Notably, it is active/running. It is different from a process in that multiple threads can share an [[address space]]. | |||
The state of a thread consists of the Program Counter and the set of register values. | |||
A '''thread control block (TCB)''' stores the states of threads to enable switching between them. | |||
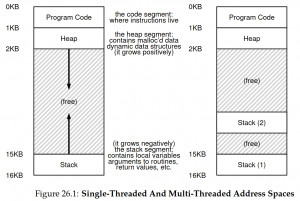
Each thread will also have its own stack, which is thus called '''thread-local storage'''. The address space diagram shows that not all stacks can grow indefinitely and may run into problems if there are lots of recursion. | |||
[[Category:Operating System]] | [[Category:Operating System]] | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 7 October 2024
A thread in Computer Science is defined as a sequence of executing instructions from a program. Notably, it is active/running. It is different from a process in that multiple threads can share an address space.
The state of a thread consists of the Program Counter and the set of register values.
A thread control block (TCB) stores the states of threads to enable switching between them.
Each thread will also have its own stack, which is thus called thread-local storage. The address space diagram shows that not all stacks can grow indefinitely and may run into problems if there are lots of recursion.
