Second Order Circuits: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 158: | Line 158: | ||
-\alpha B_1 + \omega_d B_2 = \frac{1}{C} \left( \frac{-V_0}{R} - I_0 \right) | -\alpha B_1 + \omega_d B_2 = \frac{1}{C} \left( \frac{-V_0}{R} - I_0 \right) | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
==== Characteristics ==== | |||
Voltage alternates between positive and negative values due to the two | |||
types of energy-storage elements. It's like a mass suspended on a | |||
spring. | |||
The oscillation rate is fixed by <math>\omega_d</math>, which is why it | |||
is called the '''damped radian frequency'''. | |||
The oscillation amplitude decreases exponentially at a rate determined | |||
by <math>\alpha</math>, so it is called the '''damping factor'''. | |||
Notice that when <math>R \neq 0</math>, there is <math>\alpha > 0</math> | |||
and the circuit is damped. | |||
[[Category:Electrical Engineering]] | [[Category:Electrical Engineering]] | ||
Revision as of 08:41, 8 March 2024
Second order circuits are circuits that have two energy storage elements, resulting in second-order differential equations.
One application of second order circuits is in timing computers. As we will see, an RLC circuit can generate a sinusoidal wave.
There are primarily two types of second order circuits:
- Parallel RLC circuits
- Series RLC circuits
This page will analyze them and derive some useful equations.
Series RLC Circuits
Natural Response
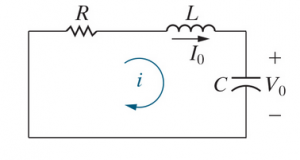
Consider an un-forced RLC circuit. We want to find .
First, we can use KVL and KCL
Next, we can use and substitution to get
Changing the order and moving the constants,
Moving constants away from the first term to get a second-order differential equation,
Parallel RLC Circuits
Natural Response
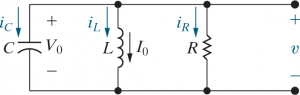
By KCL,
By differentiating once with respect to and rearranging some constants,
we get a homogeneous second-order differential equation, which has a standard solution that I will not go into detail. Briefly, it is solved by assuming since derivatives of must take the same form to cancel out to zero.
By applying the standard solution, we have
Characteristic Equation
The above simplifies to
This is the characteristic equation of the differential equation, as the root of the quadratic determines properties of
where
and
It can be pretty easily proven that the sum of the two roots is also a solution
Forms
Depending on the root, there are three forms:
- Overdamped, where there are real, distinct solutions
- Underdamped, where there are complex solutions
- Critically damped, where the solutions are not distinct.
Overdamped
For an overdamped response, we have
The A's can be solved by substituting in and
Underdamped
For an underdamped response, we have
where there is damped radian frequency
From Euler's identity, the natural response comes to
The rest is identical to that of overdamped:
Characteristics
Voltage alternates between positive and negative values due to the two types of energy-storage elements. It's like a mass suspended on a spring.
The oscillation rate is fixed by , which is why it is called the damped radian frequency.
The oscillation amplitude decreases exponentially at a rate determined by , so it is called the damping factor.
Notice that when , there is and the circuit is damped.
































