Bivariate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
Correlation is always between -1 and 1 | Correlation is always between -1 and 1. When r = 1, the relationship between X and Y is '''perfect positive linear'''. When r = -1, it is '''perfect negative linear'''. If it is 0, there is no linear relationship. This doesn't mean that there is no relationship. Notably, any symmetric scatter plot has a correlation of 0. | ||
= Bivariate Normal = | = Bivariate Normal = | ||
Revision as of 05:37, 19 March 2024
Bivariate data consider two variables instead of the usual one; each value of one of the variables is paired with a value of the other variable. We will be using to denote the two random variables throughout this page.
Summary Statistics
To summarize bivariate data, we use covariance and correlation in addition to the statistics detailed in Summary Statistics.
Covariance
The covariance measures the total variation of two RVs and their centers. It indicates the relationship of two variables whenever one changes, measuring how much the two vary together.
We have sample covariance
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s^2_{X, Y} = \hat{cov}(X, Y) = \frac{1}{n - 1} \sum(x_i - \bar{x}) (y_i - \bar{y}) = \frac{1}{n - 1} \left( \sum x_i y_i - n \bar{x} \bar{y} \right)}
A good way of thinking about covariance is by cases:
If x increases as y increases, the signs of both terms of the covariance calculation is the same. Therefore, covariance is positive.
If x decreases as y increases, the signs are different. Therefore, covariance is negative.
If x does not clearly vary with y, the signs are sometimes different, sometimes the same. Overall, it should cancel out to zero.
Correlation
The correlation of two random variables measures the line dependent between Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Cor(X, Y) = \rho = \frac{Cov(X,Y)}{sd(X) sd(Y)} }
Correlation is always between -1 and 1. When r = 1, the relationship between X and Y is perfect positive linear. When r = -1, it is perfect negative linear. If it is 0, there is no linear relationship. This doesn't mean that there is no relationship. Notably, any symmetric scatter plot has a correlation of 0.
Bivariate Normal
The bivariate normal (aka. bivariate gaussian) is one special type of continuous random variable.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (X, Y)} is bivariate normal if
- The marginal PDF of both X and Y are normal
- For any Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} , the condition PDF of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} given Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X = x} is Normal
- Works the other way around: Bivariate gaussian means that condition is satisfied
Predicting Y given X
Given bivariate normal, we can predict one variable given another. Let us try estimating the expected Y given X is x
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E(Y| X = x) }
There are three main methods
- Scatter plot approximation
- Joint PDF
- 5 statistics
5 Parameters
We need to know 5 parameters about Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E(X), sd(X), E(Y), sd(Y), \rho}
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X, Y} follows bivariate normal distribution, then we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left( \frac{E(Y|X = x) - E(Y)}{sd(Y)} \right) = \rho \left( \frac{x - E(X)}{sd(X)} \right) }
The left side is the predicted Z-score for Y, and the right side is the product of correlation and Z-score of X = x
The variance is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Var(Y | X = x) = (1 - \rho^2) Var(Y) }
Due to the range of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho} , the variance of Y given X is always smaller than the actual variance. The standard deviation is just rooted that.
Regression Effect
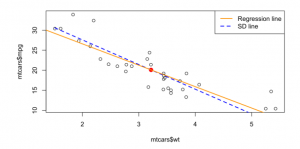
The regression effect is the phenomenon that the best prediction of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} given Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X = x} is less rare for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} ; Future predictions regress to mediocrity.
When you plot all the predicted Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E(Y|X = x)} , you get the linear regression line. The regression effect can be demonstrated by also plotting the SD line (where the correlation is not applied).
Linear Regression
Assumption
- X and Y have a linear relationship
- A random sample of pairs was taken
- All pairs of data are independent
- The variance of the error is constant. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Var(\epsilon) = \sigma_\epsilon^2}
- The average of the errors is zero. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E(\epsilon) = 0}
- The errors are normally distributed.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon \sim^{iid} N(0, \sigma_\epsilon^2), Y_i \sim^{iid} N(\beta_0 + \beta_1 x_i, \sigma_\epsilon^2) }
Procedure
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y_i = \beta_0 + \beta_1 x_i + \epsilon_i }
where the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_0, \beta_1} are regression coefficients (slope, intercept) based on the population, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_i} is error for the i-th subject.
We want to estimate the regression coefficients.
Let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{y_i}} be an estimation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y_i} ; a prediction at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X = x} , with
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{y_i} = \hat{\beta_0} + \hat{\beta_1} x_i }
We can measure the vertical error Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e_i = y_i - \hat{y_i}}
The overall error is the sum of squared errors Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle SSE = \sum_i^n e_i^2} . The best fit line is the line minimizing SSE.
Using calculus, we can find that the line has the following scope and intercept:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{\beta_1} = r \frac{s_y}{s_x} }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} is the strength of linear relationship, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_x, s_y} is the deviations of the sample. They are basically the sample versions of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho, \sigma}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{\beta_0} = \bar{Y} - \hat{\beta_1} \bar{X} }
Interpretation
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_1} (the slope) is the estimated change in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} changes by one unit.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_0} (the intercept) is the estimated average of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X = 0} . If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} cannot be 0, this may not have a practical meaning.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r^2} (coefficient of determination) measures how good the line fits the data.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r^2 = \frac{\sum (\hat{y_i} - \bar{Y})^2 }{\sum (y_i - \bar{Y})^2} }
The bottom is total variance. The top is reduced. The value is the proportion of variance in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} that is explained by the linear relationship between Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Y} .

