Artificial neural network: Difference between revisions
From Rice Wiki
(Created page with "An '''artificial neural network (ANN)''' is a machine learning algorithm that uses three layers of neurons to perform classification/regression. = Structure = All ANN's consist of three layers of neurons: the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer. The number of neurons in each layer determines the complexity of the model, with a larger layer indicating a more complicated model. Each neuron takes in information from neurons of the previous layer (and for t...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
= Loss function = | = Loss function = | ||
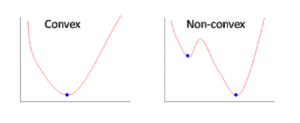
[[File:Covex vs. Non-convex.png|thumb|Figure 1. Convex vs. non-convex loss function. Non-convex has local minimums that needs to be filtered out.]] | |||
The loss function in ANN is usually ''non-convex'', making minimization more difficult than setting the gradient to 0. | The loss function in ANN is usually ''non-convex'', making minimization more difficult than setting the gradient to 0. | ||
Revision as of 23:31, 30 April 2024
An artificial neural network (ANN) is a machine learning algorithm that uses three layers of neurons to perform classification/regression.
Structure
All ANN's consist of three layers of neurons: the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer. The number of neurons in each layer determines the complexity of the model, with a larger layer indicating a more complicated model.
Each neuron takes in information from neurons of the previous layer (and for the case of the input layer, the input). An ANN is considered dense if each neuron takes input from every neuron of the previous layer.
Loss function
The loss function in ANN is usually non-convex, making minimization more difficult than setting the gradient to 0.
